Pronouns are essential building blocks of language that make our sentences more efficient. Understanding pronouns and ways to use them correctly is crucial for clear communication. In this article, we will dive into the different types of pronouns and provide examples to help you grasp their usage.
What is a Pronoun?
A pronoun is a word that replaces a noun in a sentence. It helps avoid repetition and make sentences sound more natural. For example, instead of saying, “Sarah likes Sarah’s book,” you can say, “Sarah likes her book.” The word “her” is a pronoun that replaces “Sarah’s.”
Types of Pronouns
There are several types of pronouns, each serving a unique purpose in a sentence. Let us explore the different types and their examples.
- Personal Pronouns
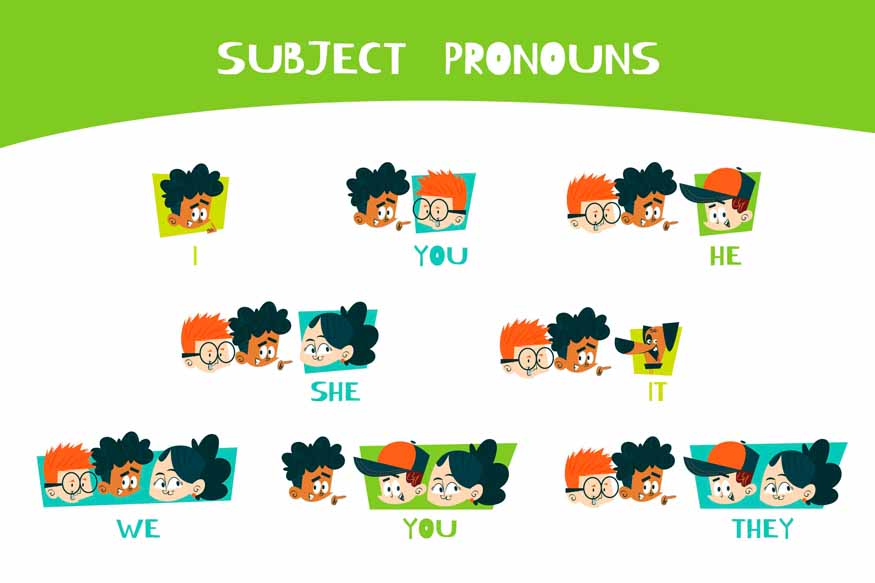
- Subject Pronouns: Used as the subject of a sentence.
- Examples: I, you, he, she, it, we, they
- Sentence: She is going to the store.
- Object Pronouns: Used as the object of a sentence.
- Examples: me, you, him, her, it, us, them
- Sentence: The teacher helped him with his homework.
- Possessive Pronouns: Show ownership or possession.
- Examples: mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs
- Sentence: The book is mine.
- Reflexive Pronouns
- Examples: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves
- Sentence: He taught himself to play the guitar.
- Demonstrative Pronouns
- Examples: this, that, these, those
- Sentence: These are my favourite cookies.
- Interrogative Pronouns
- Examples: who, whom, whose, which, what
- Sentence: Whose jacket is this?
- Relative Pronouns
- Examples: who, whom, whose, which, that
- Sentence: The book that you lent me was fascinating.
- Indefinite Pronouns
- Examples: anyone, everyone, someone, no one, anything, everything, something, nothing
- Sentence: Someone left their umbrella in the classroom.
Personal pronouns refer to specific people or things and are used to avoid repeating names. They can be classified into subject pronouns, object pronouns, and possessive pronouns.
Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and object of a sentence are the same person or thing. They end in “-self” or “-selves.”
Demonstrative pronouns point to specific things or people. They help identify and specify which one is being referred to.
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions. They help gather information about people or things.
Relative pronouns connect clauses or phrases to a noun or pronoun. They introduce relative clauses, which provide more information about the noun.
Indefinite pronouns refer to nonspecific people or things. They are useful when the exact identity is unknown or not important.
Teaching Pronouns to Kids
Teaching pronouns to kids can be fun and interactive. Here are some strategies to make learning about pronouns enjoyable and effective.
- Use Visual Aids
- Interactive Games
- Pronoun Matching: Create cards with nouns and corresponding pronouns. Have kids match the nouns with the correct pronouns.
- Pronoun Bingo: Make bingo cards with different pronouns. Call out sentences, and kids mark the pronouns on their cards. The first to get a bingo wins!
- Pronoun Scavenger Hunt: Hide objects around the room and provide clues using pronouns. For example, “Find the object that is hers.”
- Storytelling
- Pronoun Worksheets
- Songs and Rhymes
Visual aids like charts, flashcards, and posters can help kids understand pronouns better. Create a colourful chart with different types of pronouns and their examples. Display it in the classroom or study area for easy reference.
Pronouns Chart
|
Type of Pronoun |
Examples |
|
Subject Pronouns |
I, you, he, she, it, we, they |
|
Object Pronouns |
me, you, him, her, it, us, them |
|
Possessive Pronouns |
mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs |
|
Reflexive Pronouns |
myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves |
|
Demonstrative Pronouns |
this, that, these, those |
|
Interrogative Pronouns |
who, whom, whose, which, what |
|
Relative Pronouns |
who, whom, whose, which, that |
|
Indefinite Pronouns |
anyone, everyone, someone, no one, anything, everything, something, nothing |
Games are a great way to reinforce learning. Here are a few fun games to teach pronouns:
Encourage kids to create stories using pronouns. Provide them with a list of pronouns and ask them to write or tell a story that includes as many pronouns as possible. This activity helps kids practice using pronouns in context.
Worksheets are a useful tool for practising pronouns. Create worksheets with fill-in-the-blank sentences, pronoun identification exercises, and pronoun usage tasks. This allows kids to apply their knowledge and receive feedback.
Songs and rhymes are a fun way to memorize pronouns. Create a catchy song or rhyme that includes different types of pronouns and their examples. Sing it together to reinforce learning.
Pronoun Song Example: (To the tune of “Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star”)
“I and you, he and she, It and we, they and me. These are pronouns, can’t you see? Use them in a sentence, like me!”
Fascinating Facts About Pronouns
- Fun Fact: The word “pronoun” comes from the Latin word “pronomen,” meaning “for a noun.”
- Interesting Titbit: The English language has over 100 different pronouns!
- Cool Insight: In some languages, gender-neutral pronouns do not specify male or female.
Pronouns with Examples
|
Pronoun Type |
Examples |
Usage |
|
Subject Pronouns |
I, you, he, she, it, we, they |
Used as the subject of a sentence |
|
Object Pronouns |
me, you, him, her, it, us, them |
Used as the object of a sentence |
|
Possessive Pronouns |
mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs |
Show ownership or possession |
|
Reflexive Pronouns |
myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves |
Reflect the action back to the subject |
|
Demonstrative Pronouns |
this, that, these, those |
Point to specific things or people |
|
Interrogative Pronouns |
who, whom, whose, which, what |
Used to ask questions |
|
Relative Pronouns |
who, whom, whose, which, that |
Connect clauses or phrases to a noun or pronoun |
|
Indefinite Pronouns |
anyone, everyone, someone, no one, anything, everything, something, nothing |
Refer to nonspecific people or things |
For more such informative/interesting blogs, visit Center Point School.